How to lock down Remote Desktop Protocol servers

Make sure you've made all the proper settings to secure RDP to best protect your Windows network when supporting remote workers.
All employees are logging in from home. Your connections are holding up well enough, but you’re likely concerned that it’s not enough to keep your network safe from the attackers. Many organizations have turned to Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) to enable remote connections. These steps will better lock down those connections.
The basics: Patching, VPNs and strong passwords
Ensure that all remote machines connecting with the network are patched to include those for the most recent RDP vulnerabilities. That should include Windows 7 workstations as well. You can buy Windows 7 Extended Security Updates (ESUs) in any quantity. If you have placed a Windows 7 workstation back into service to give a home user access, you have no excuse to not patch that machine.
Next, allow only RDP combined with a VPN. Never expose port 3389 directly to the web. Ransomware attackers will “sniff” the outbound transmissions of a location and use tools such as TSgrinder to brute force the credentials of an RDP location. Never allow outbound port 3389 connectivity unless it has restrictions set in the inbound firewall rules to restrict access to certain static IPs under your control.
Enforce a strong password policy. Encourage your users to not reuse passwords. Remind them of breaches that have exposed passwords that are now in the hands of attackers. Ensure that users do not save the password to their RDP-connected computer.
Consider adding two-factor authentication (2FA) to remote desktops. Many vendors offer solid 2FA options, and some are offering extended free trials at this time.
Enable Network Level Authentication for RDS servers
Recent advice for mitigating the BlueKeep vulnerability says that RDP should never be exposed publicly. It’s hard for some companies to follow that advice now. Network Level Authentication (NLA) forces users to authenticate before connecting to remote systems, which dramatically decreases the chance of success for RDP-based worms.
While Windows 10 enables NLA by default, older platforms may not. Use Group Policy to set NLA on the host platform and Remote Desktop Services. From Group Policy, select the following in this order:
- Computer
- Policies
- Windows Components
- Remote Desktop Services
- Remote Desktop Session Host
- Security
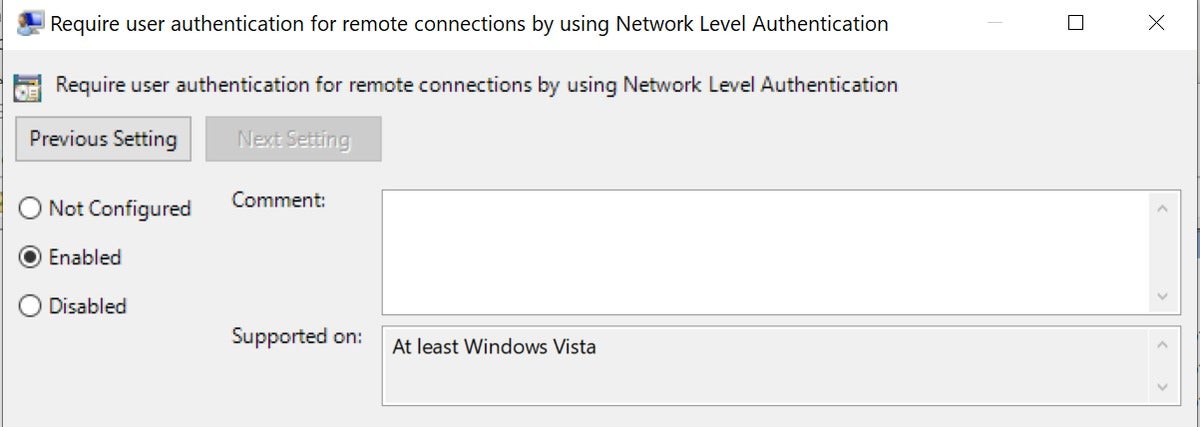
Enable “Require user authentication for remote connections by using Network Level Authentication” on servers running the Remote Desktop Session Host role.
Enable NLA
Disable shut-down for users
When new users log into an RDP server, they don’t realize that their actions on the remote machine impact all users in the environment. That’s why it’s important to disable the ability for users to shut down the machine by following these steps:
- On the RDP server host machine, click on “Start”.
- Click on “Run”.
- Enter
gpedit.msc. - Go to “User Configuration then to Administrative Templates”.
- Go to “Start Menu and Taskbar”.
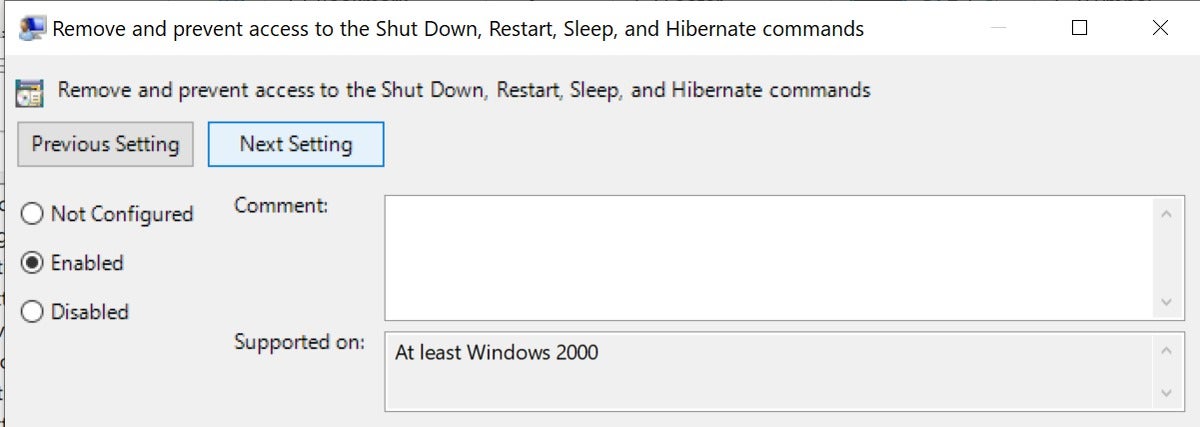
- Click on “Remove and prevent access to the Shut Down, Restart, Sleep, and Hibernate commands”.
- Enable the setting.
Disable shut-down
If you wish some administrative users to have the ability to reboot, follow these steps:
- Log in with administrative rights.
- Click on “Start”.
- Click on “Run”.
- Enter secpol.msc to enter the Security Policy Editor.
- Go to “Local policy”.
- Go to “User Right Assignment”.
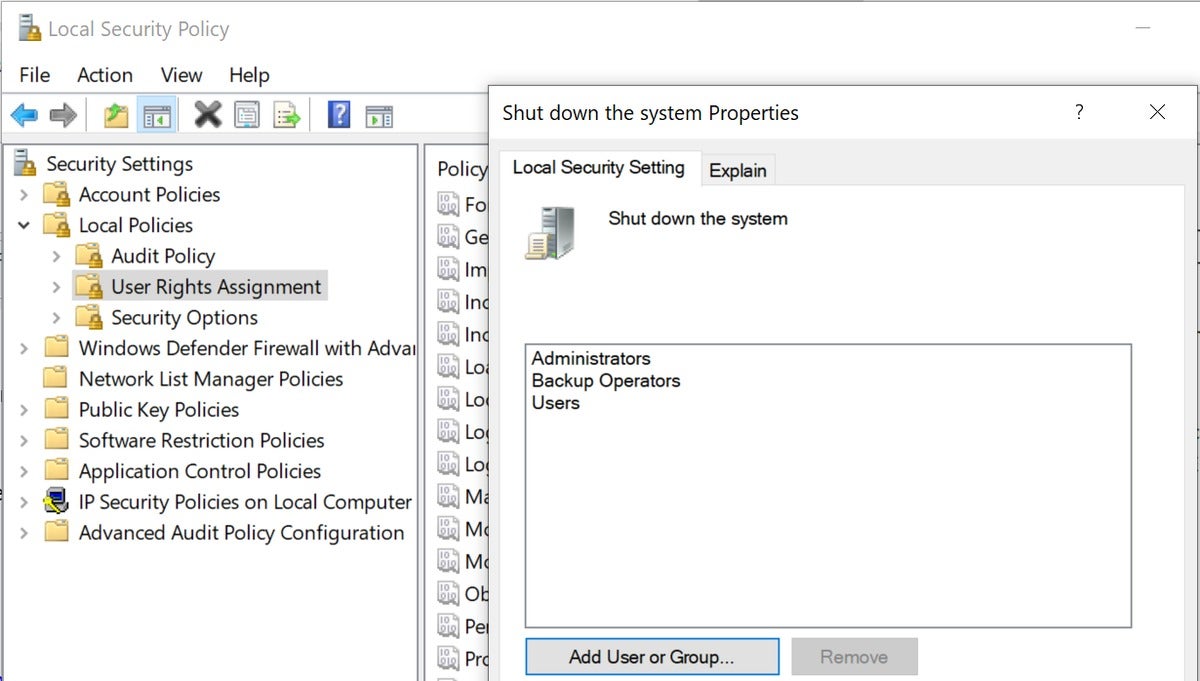
- Go to “Shut down the system”.
- Right-click on “Properties”.
- Remove the user and then add the admin user or admin group you wish to have the ability to reboot the system.
Adjust RDP for performance
Performance tweaks
When deploying RDP, if the user experience is not acceptable, users find ways to work around bottlenecks including security risks like emailing files to personal email accounts. Fine-tune the performance settings with these steps in Group Policy:
- Go to “Computer Configuration”.
- Go to “Administrative Templates”.
- Go to “Windows Components”.
- Go to “Remote Desktop Services”.
- Go to “Remote Desktop Session Host”.
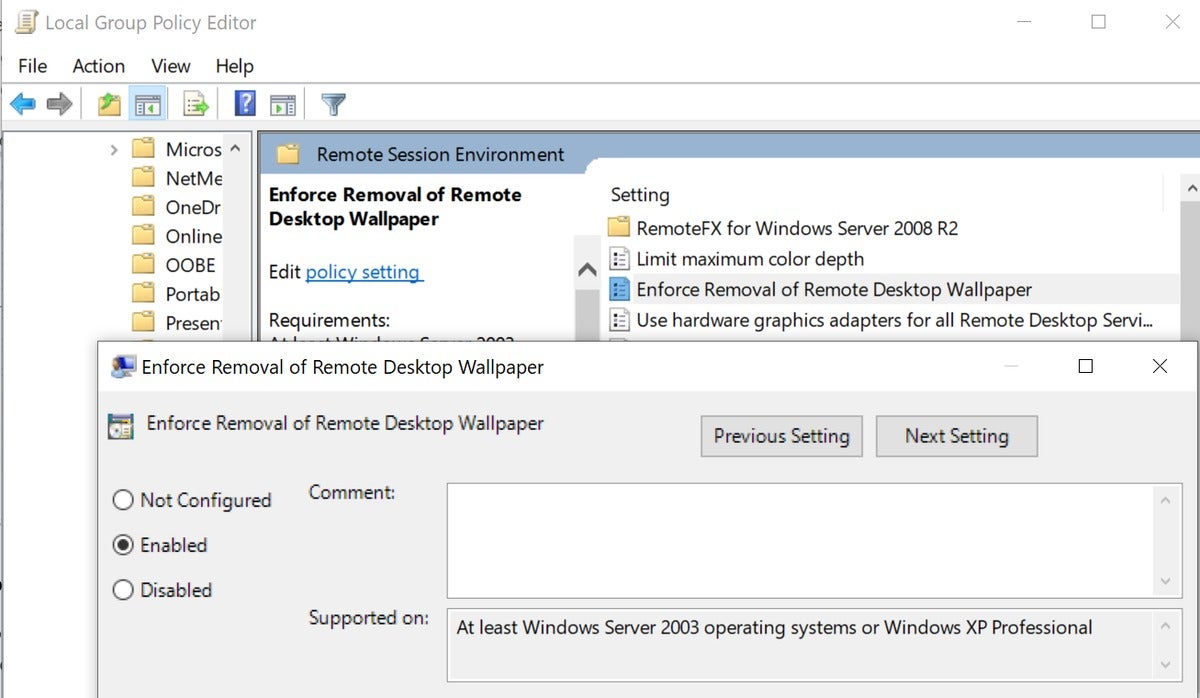
- Go to “Remote Session Environment”
You’ll want to adjust the following settings:
- Limit maximum color depth = 15bit
- Enforce Removal of Remote Desktop wallpaper = true
- Optimize Visual Experience when using RemoteFx = (Screen Capture Rate: Lowest + Image Quality: Lowest)
- Set Compression Algorithm for RDP data = optimized to use less network bandwidth
- Optimize Visual Experience for Remote Desktop Service Sessions = (Visual Experience = Text)
- Configure Image Quality for RemoteFx Adaptive Graphics = Medium
- Configure RemoteFx Adaptive Graphics = Optimize for minimum bandwidth usage
Give admins the ability to reboot
Under “Device and Resource Redirection”, you can limit clipboard redirection, drive redirection, LPT port redirection or any other settings appropriate for your organization. Under “Printer Redirection”, you can allow users to redirect the printers to their local machines. I have not found major issues when using remote printing even when printers are connected via USB connections.
SSL/TLS settings
When configuring SSL and TLS on your server, be careful about the settings on RDP servers. Setting these SSL settings incorrectly can lock users out. In particular, if you’ve disabled TLS 1.0 from a Windows 7 machine or Server 2008, you need to update the RDP client to RDP 8.1.
For Server 2008 R2, you will need a patch to support TLS 1.1 or 1.2 for RDP. Install KB3080079 to support the higher TLS settings. Set a Group Policy object that disables SSL 1.0, 2.0, 3.0 and TLS 1.0 via registry keys and explicitly enables TLS 1.1. and TLS 1.2 for both server and client settings as noted in this blog. You can also use IISCrypto to set and review the TLS settings. If you use RDgateway, review the SSL settings externally using an SSL test. Review KB245030 to restrict the cyphers that are being used in your organization.
Deploy virtual desktops
Microsoft has a new offering called Windows Virtual Desktop. Firms are accelerating their moves to Windows Virtual Desktop as a result of work-from-home mandates. This video from March 19 shows how to accelerate deployment.